 이미지 확대보기
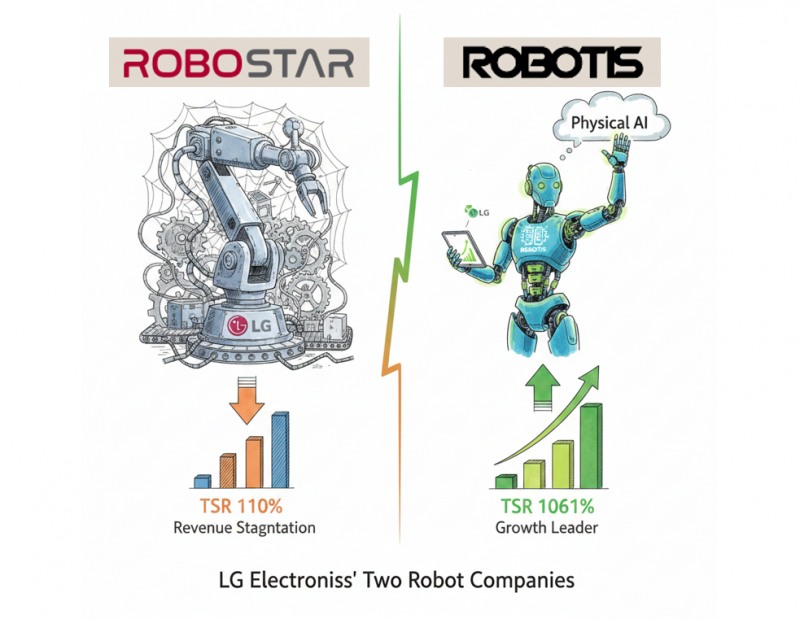
이미지 확대보기As the robot industry emerges as a government-led nurturing sector and related stocks stir, shareholder performance reports of two robot companies with equity relationships with LG Electronics have sharply diverged. These are Robostar and ROBOTIS.
Korea Financial Times analyzed 'Cumulative Total Shareholder Return (TSR),' a return indicator combining stock price changes and dividend yields over a certain period, to compare returns from a shareholder perspective for the two companies.
For Robostar, calculations were made from July 17, 2018, when LG Electronics completed its stake acquisition, to October 30, 2025. For ROBOTIS, since LG Electronics purchased shares on January 12, 2018, before listing, calculations were made from the listing date of October 26, 2018, to the end of October.
The analysis showed Robostar at 110.77% and ROBOTIS at 1,061.52%. Although both companies either formed ties with LG Electronics or went public in 2018, shareholder returns over approximately 7-8 years differed by nearly tenfold.
This means that if someone had invested KRW 1 million each in Robostar and ROBOTIS at that time and held for about 8 years, they would have made KRW 1 million from Robostar but over KRW 10 million from ROBOTIS.
This difference originated from stock prices. Robostar's cumulative stock price appreciation rate was 108.09%, while ROBOTIS recorded 1,055.24%. Cumulative dividend yield also showed ROBOTIS ahead at 6.29% versus Robostar's 2.87%.
Robostar was established in 1999 by engineers who left LG Industrial Systems (now LS Electric). It focuses on industrial robots and automation equipment used in manufacturing processes such as displays, semiconductors, and secondary batteries.
It generates stable revenue by absorbing smart factory demand from group affiliates such as LG Electronics, LG Energy Solution, and LG Display. Limitations include non-explosive growth in the manufacturing industrial robot market and intensifying global competition.
According to Nice Information Service's technology analysis report, the industrial robot market is dominated by global companies such as Japan's Fanuc and Yaskawa. While Robostar competes with price competitiveness and delivery responsiveness, weak brand awareness and overseas market expandability, and a structure where performance is linked to manufacturing facility investment cycles are cited as weaknesses.
Recently, Robostar has been affected as front-end industry investment has been delayed due to high interest rates and the electric vehicle chasm (temporary demand slowdown).
Robostar emerged from operating losses in 2020 and has maintained profitability since 2021. Revenue increased from KRW 132 billion in 2020 to KRW 142.5 billion in 2021 and KRW 143.2 billion in 2022, then decreased to KRW 102.7 billion in 2023 and KRW 89.1 billion in 2024.
Operating profit recorded a loss of KRW 11.3 billion in 2020, turned to profit at KRW 0.2 billion in 2021, expanded to KRW 1.8 billion in 2022, but decreased to KRW 1.1 billion in 2023 and KRW 0.1 billion in 2024. In Q3 2025, revenue was KRW 17.3 billion and operating loss was KRW 1.1 billion, with revenue increasing 1.76% year-over-year while the deficit narrowed.
However, a rebound is expected starting this year. Increased secondary battery line automation demand following electric vehicle and Energy Storage System (ESS) market expansion, resumption of Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) facility investment, and government smart factory support policies are forecast to be catalysts for performance recovery.
ROBOTIS is a company where the core component 'Dynamixel,' which serves as robot joints, accounts for approximately 98% of revenue. Recently, as the robot market moves toward Physical AI, ROBOTIS's corporate value is being re-evaluated. Physical AI refers to robots that move and judge flexibly like humans, with actuators being essential components.
ROBOTIS is expanding its business area by recently developing the humanoid robot 'AI Worker.' AI Worker is a robot that mimics skilled work to perform high-difficulty tasks at low cost. The company signed a 'humanoid robot joint research and commercialization' agreement with LG Electronics in June and delivered research products.
The autonomous driving robot business is also expanding. While actuator sales proportion decreased from 99.62% in 2023 to 98.47% in 2024, autonomous driving robots increased from 0.38% to 1.53% during the same period.
ROBOTIS continued annual operating losses from listing through 2024. However, revenue maintained growth at KRW 19.2 billion in 2020, KRW 22.4 billion in 2021, KRW 25.9 billion in 2022, and KRW 30 billion in 2024. Operating loss scale was KRW 1.8 billion in 2020, KRW 0.9 billion in 2021, KRW 2.2 billion in 2022, KRW 5.3 billion in 2023, and KRW 3 billion in 2024.
Cumulative revenue for the first three quarters of 2025 increased 17.5% year-over-year to KRW 27.3 billion, with operating profit turning to black at KRW 2.3 billion. According to Daishin Securities Research Center, ROBOTIS is forecast to achieve annual profitability by recording KRW 1.8 billion in operating profit for the year.
Lee Ji-ni, an analyst at Daishin Securities, stated, "Due to domestic industrial characteristics with high manufacturing proportion, government-led robot automation rates will increase through 2030, and actuator demand will also grow," and "As the global robot industry blossoms into Physical AI and robot hand demand increases, ROBOTIS actuator sales volume will also grow."
Shin Haeju (hjs0509@fntimes.com)
[관련기사]
- Can LG Electronics Maintain an Operating Margin of 4% in Q2?
- LG Group, 'Electronics' Defensive Power Draws Attention Amid 'Chemical' Crisis
- Hyundai Motor Group 'Chung Eui-sun era' 5 years ②: 'Bold strategist' Chung Eui-sun to break through with KRW 112 trillion investment over next 5 years
- Hyundai Motor Group 'Chung Eui-sun era' 5 years ①: 'Disruptive innovation leadership' powers global Big3
- Hyundai Glovis · AutoEver rally boosts Chung succession bid
가장 핫한 경제 소식! 한국금융신문의 ‘추천뉴스’를 받아보세요~
데일리 금융경제뉴스 Copyright ⓒ 한국금융신문 & FNTIMES.com
저작권법에 의거 상업적 목적의 무단 전재, 복사, 배포 금지












![Robot Joints, 80%-a-Year Growth: Hyundai Mobis, Samsung Electro-Mechanics Lead Korea's Actuator Rush [K-Humanoid Wars ④]](https://cfnimage.commutil.kr/phpwas/restmb_setimgmake.php?pp=006&w=284&h=214&m=5&simg=2026030908365902517141825007d12411124362.jpg&nmt=18)


!['From Heavy Industry to Humanoids' — Doosan Robotics Charts a New Future in Physical AI [K-Humanoid Wars, Part 3]](https://cfnimage.commutil.kr/phpwas/restmb_setimgmake.php?pp=006&w=284&h=214&m=5&simg=2026030310061306979141825007d12411124362.jpg&nmt=18)

!['Samsung's Bet on the Future' — Rainbow Robotics, Korea's Humanoid Pioneer [K-Humanoid Wars, Part 2]](https://cfnimage.commutil.kr/phpwas/restmb_setimgmake.php?pp=006&w=284&h=214&m=5&simg=2026022413501808272141825007d12411124362.jpg&nmt=18)
![Tesla's Humanoid Rival Has Arrived — Boston Dynamics Eyes $70 Billion Valuation [K-Humanoid Wars, Part 1]](https://cfnimage.commutil.kr/phpwas/restmb_setimgmake.php?pp=006&w=284&h=214&m=5&simg=2026022010243207659141825007d12411124362.jpg&nmt=18)
![Tesla's Humanoid Rival Has Arrived — Boston Dynamics Eyes $70 Billion Valuation [K-Humanoid Wars, Part 1]](https://cfnimage.commutil.kr/phpwas/restmb_setimgmake.php?pp=006&w=110&h=79&m=5&simg=2026022010243207659141825007d12411124362.jpg&nmt=18)
!['Samsung's Bet on the Future' — Rainbow Robotics, Korea's Humanoid Pioneer [K-Humanoid Wars, Part 2]](https://cfnimage.commutil.kr/phpwas/restmb_setimgmake.php?pp=006&w=110&h=79&m=5&simg=2026022413501808272141825007d12411124362.jpg&nmt=18)


!['From Heavy Industry to Humanoids' — Doosan Robotics Charts a New Future in Physical AI [K-Humanoid Wars, Part 3]](https://cfnimage.commutil.kr/phpwas/restmb_setimgmake.php?pp=006&w=110&h=79&m=5&simg=2026030310061306979141825007d12411124362.jpg&nmt=18)